Dental restorations play a vital role in restoring damaged, weakened, or missing teeth while maintaining oral function, appearance, and long-term dental health. From dental crowns and dental bridges to advanced material science and modern dental lab workflows, restorative dentistry combines clinical expertise with precision manufacturing.
This pillar page explains what a dental crown is, types of dental crowns, dental crown procedures, bridges vs crowns, and how dental materials like zirconia are used within the dental lab process. Each section naturally supports and connects with the TOFU blogs mapped under this silo.
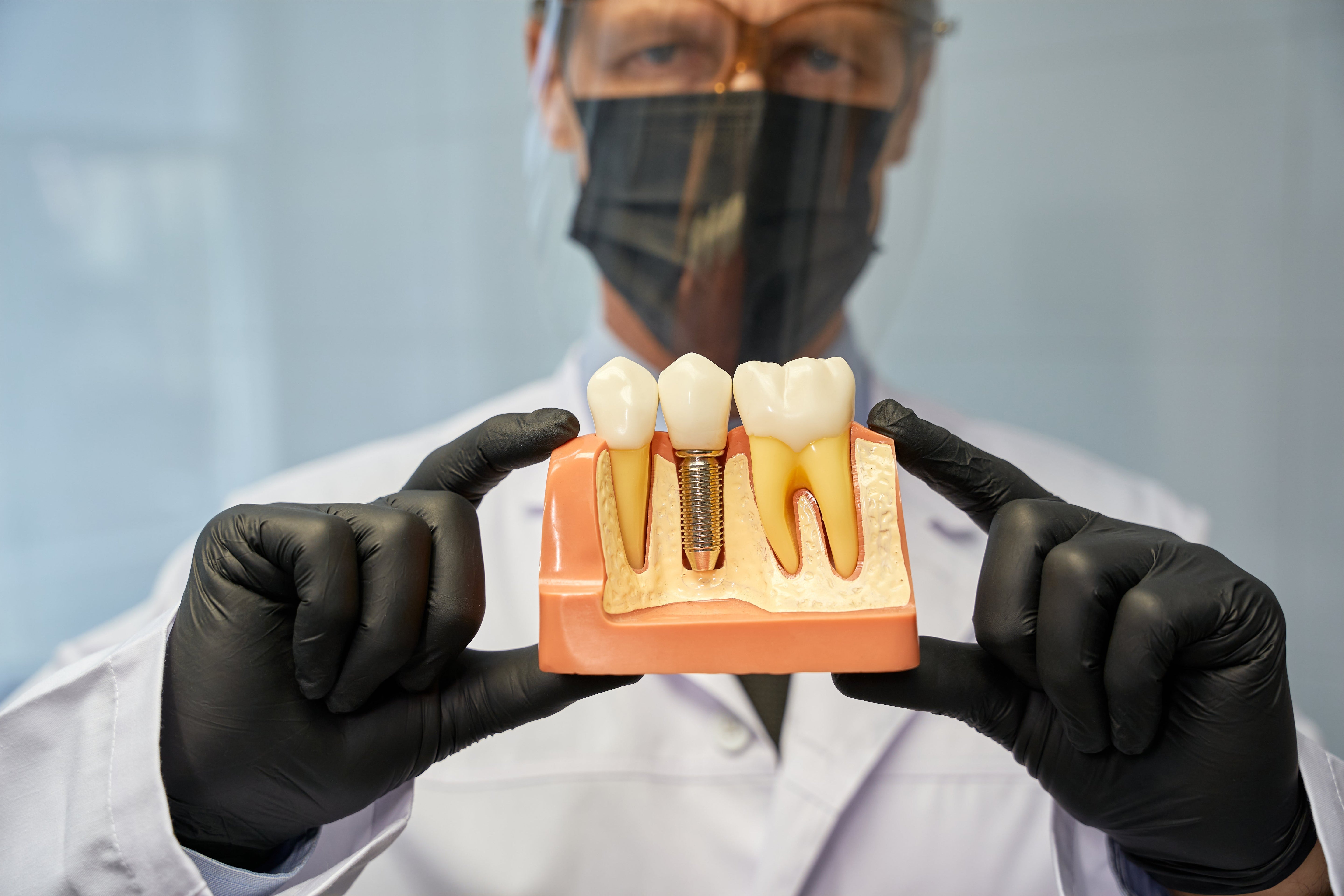
What Is a Dental Crown?
A common starting point in restorative dentistry is understanding what is a dental crown. A dental crown is a tooth-shaped cap placed over a damaged, decayed, or weakened tooth to restore its shape, strength, and appearance.
Dental crowns are widely used when:
- A tooth is cracked or heavily filled
- After root canal treatment
- To support dental bridges
- For esthetic improvement
Modern aidite zirconia crowns and zirconium dental crowns are fabricated using advanced CAD CAM dentistry, ensuring precision and durability.
Types of Dental Crowns Explained
There are several dental crown types, each suited for different clinical needs. Understanding the types of dental crowns helps patients and professionals choose the right restoration.
Common dental crown materials include:
- Zirconia crowns
- Porcelain-fused-to-metal
- All-ceramic crowns
- Metal crowns
Comparisons such as porcelain vs zirconia crowns and ceramic vs zirconia crowns highlight why zirconia dental material is widely preferred today due to strength and esthetics.
Dental Crown Treatment Process
The dental crown procedure typically involves:
- Tooth preparation
- Impression or digital scan
- Temporary crown placement
- Final crown cementation
Today, digital dentistry and CAD CAM dental lab workflows streamline this process. Dental labs use dental milling machines, zirconia blocks, and zirconia dental blanks to produce accurate restorations.
Dental Crown vs Dental Cap
Patients often ask about dental crown vs dental cap. In simple terms:
- Both terms mean the same restoration
- “Cap” is a non-technical term
- “Crown” is the clinical term
Regardless of terminology, crowns rely on dental lab materials and precise fabrication within a professional dental lab.
How Long Do Dental Crowns Last?
The lifespan of dental crowns depends on:
- Crown material
- Bite forces
- Oral hygiene
- Dental lab quality
High-quality zirconia crowns fabricated using zirconia multilayer, zirconia disc, and dental zirconia discs can last 10–15 years or longer.
Dental Bridges Explained
Dental bridges are restorations used to replace missing teeth by anchoring artificial teeth between crowns. Understanding types of dental bridges helps in choosing the right option.
Common bridge types include:
- Traditional bridges
- Cantilever bridges
- Implant-supported bridges
Comparisons such as dental crown vs bridge and dental bridge vs implant help determine the best solution based on bone health and longevity.
- Dental Crown vs Bridge
- What Is a Dental Bridge and How Does It Work?
Are Dental Crowns Permanent or Replaceable?
While dental crowns are long-term restorations, they are not permanent for life. Over time, wear, gum recession, or material fatigue may require replacement. Using premium zirconia dental material improves longevity and reduces complications.
Common Dental Crown Problems and Solutions
Some common issues include:
- Poor fit
- Bite discomfort
- Chipping or fracture
- Gum irritation
Modern dental lab processes, precision dental milling, and high-quality zirconia multilayer discs minimize these risks significantly.
Dental Crown Aftercare and Maintenance
Proper aftercare ensures crown longevity:
- Maintain oral hygiene
- Avoid excessive biting forces
- Schedule regular dental check-ups
Patients with zirconia crowns benefit from smooth surfaces that resist plaque accumulation.
Dental Veneers vs Crowns: What’s the Difference?
Dental veneers and crowns serve different purposes. When comparing veneers vs crowns:
- Veneers are thin shells for cosmetic improvement
- Crowns cover the entire tooth for strength
Zirconia dental material allows both restorations to achieve natural esthetics with durability.
Understanding Dental Materials in Restorations
Modern restorations rely on advanced dental materials. Understanding types of dental materials explains why zirconia dominates restorative dentistry.
Key materials include:
- Zirconia dental material
- Zirconia blocks dental
- Zirconium block
- Zirconia blanks
- Zirconia dental blanks
Dental labs source these from trusted dental lab material suppliers and zirconia dental material suppliers, often choosing zirconia blocks wholesale to manage zirconia blocks price efficiently.
Dental Lab Process: From Design to Final Crown
A modern dental lab process involves:
- Digital impressions
- CAD CAM dentistry design
- Dental milling
- Sintering and finishing
Understanding dental lab vs clinic roles clarifies that clinics diagnose and treat, while dental labs manufacture restorations using dental milling machines and precision materials.
Why Zirconia Is Widely Used in Dentistry
Knowing what is zirconia in dentistry explains its popularity:
- High strength
- Biocompatibility
- Esthetic translucency
- Ideal for digital dentistry
Zirconia is used across crowns, bridges, and implant restorations, making it a cornerstone of modern dental restorations.