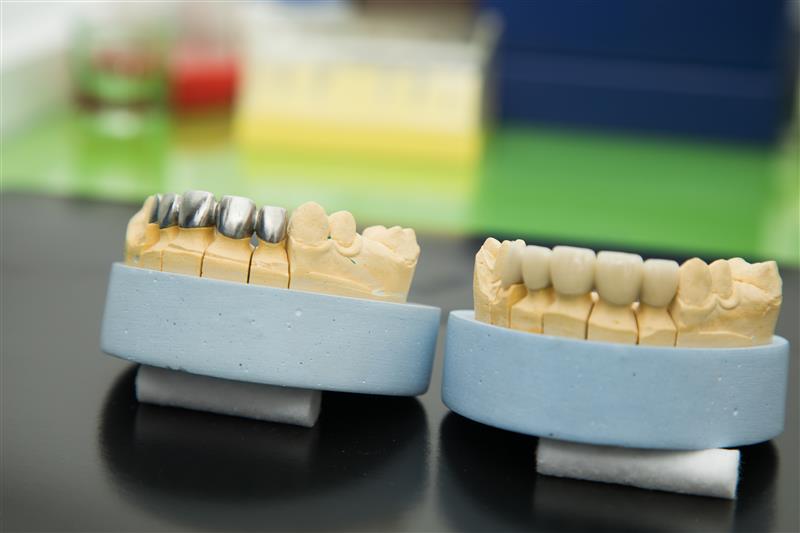
Choosing the right dental crown material is a balance between strength, esthetics, and clinical requirements. With advances in digital dentistry, dental labs now fabricate crowns using highly specialized dental lab materials designed for accuracy and durability. This guide compares the most common dental crown materials used today.
Overview of Dental Crown Materials
Modern dental materials fall into three main categories:
- Zirconia dental material
- Ceramic-based materials
- PMMA and provisional materials
Each serves a distinct purpose within restorative dentistry.
Zirconia Dental Material
Zirconia dental material is widely used for permanent crowns due to its superior strength and esthetics. Zirconia crowns are fabricated from:
- Zirconia blocks
- Zirconium block formats
- Zirconia multilayer discs
- Dental zirconia discs
Zirconia blanks offer consistency, making them ideal for high-precision CAD CAM dental lab workflows.
Advantages of Zirconia Crowns
- Excellent fracture resistance
- Suitable for anterior and posterior use
- Long lifespan
- Minimal chipping risk
Ceramic Crown Materials
Ceramic crowns offer good esthetics but may lack the strength needed for posterior restorations. Ceramic vs zirconia crowns comparisons often highlight zirconia’s superior durability.
Ceramic materials are still used for low-stress anterior cases but are gradually being replaced by zirconia crowns.
PMMA Crown Materials
PMMA crowns are commonly used for:
- Temporary crowns
- Try-ins
- Provisional restorations
While PMMA lacks the strength for permanent use, it plays an essential role in treatment planning and digital workflows.
Zirconia Multilayer Technology
Zirconia multilayer materials provide natural shade gradients from cervical to incisal areas. These materials reduce manual staining and improve esthetic consistency across restorations.
Multilayer zirconia is fabricated from advanced zirconia dental blanks and zirconia disc systems.
Digital Dentistry and Material Selection
Digital dentistry allows dental labs to optimize material use through:
- CAD CAM dentistry
- Dental milling machines
- Precision sintering cycles
Dental lab material suppliers play a key role in providing consistent zirconia blocks price and quality.
Dental Crown Cost vs Material Choice
Dental crown cost is influenced by:
- Material type
- Manufacturing process
- Dental lab expertise
Zirconia crowns may have a higher upfront cost but offer superior longevity, reducing long-term replacement needs.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Crown
The best material selection depends on:
- Functional requirements
- Esthetic expectations
- Dental lab capabilities
- Patient budget
Zirconia dental material remains the most versatile choice for permanent restorations.
To gain a broader perspective on restorative material science and how different options compare across clinical and laboratory workflows, explore the pillar resource Dental Materials Explained: Ceramics, Zirconia, PMMA & More. This comprehensive guide covers dental ceramics, zirconia dental material, PMMA restorations, and the role of modern dental lab materials in supporting precise, CAD/CAM-driven crown fabrication.
Conclusion
When comparing dental crown materials, zirconia consistently stands out for its strength, esthetics, and digital compatibility. As dental labs continue adopting CAD CAM workflows, zirconia blocks and zirconia dental blanks will remain central to restorative dentistry.
For dental labs aiming to achieve consistent results across permanent and provisional restorations, material sourcing is just as important as material selection. Zirconia Guys supports modern digital dentistry by supplying reliable dental lab materials, including zirconia blocks, zirconia dental blanks, zirconia multilayer discs, and PMMA solutions used across CAD/CAM crown workflows. By providing dependable zirconia dental material with consistent quality and transparent zirconia blocks price structures, Zirconia Guys helps labs deliver durable, esthetic crowns with predictable long-term performance.